FieldTrip stats demo
In this demonstration we will use the face recognition dataset.
Please use the general instructions to get started.
Part 1 - explore a simple contrast
datadir = '../data'; % CHANGE THIS FOR THE CORRECT LOCATION OF THE DATA
subj = 15; % CHANGE THIS NUMBER FOR EACH SUBJECT
%% read the data from all separate runs
% this will contain the runs for a single subject
rundata = {};
for run=1:6
trialdef = fullfile(datadir, sprintf('Sub%02d', subj), 'MEEG', 'Trials', sprintf('run_%02d_trldef.txt', run));
dataset = fullfile(datadir, sprintf('Sub%02d', subj), 'MEEG', sprintf('run_%02d_sss.fif', run));
[begsample, endsample, offset, trialtype] = textread(trialdef, '%d%d%d%s');
trialcode = nan(size(trialtype));
trialcode(strcmp(trialtype, 'Famous')) = 1;
trialcode(strcmp(trialtype, 'Unfamiliar')) = 2;
trialcode(strcmp(trialtype, 'Scrambled')) = 3;
% construct the trial definition matrix, usually done with FT_DEFINETRIAL
trl = [begsample(:) endsample(:) offset(:) trialcode(:)];
cfg = [];
cfg.dataset = dataset;
cfg.trl = trl;
% MEG specific settings
cfg.channel = 'MEG';
cfg.demean = 'yes';
data_meg = ft_preprocessing(cfg);
% EEG specific settings
cfg.channel = 'EEG';
cfg.demean = 'yes';
cfg.reref = 'yes';
cfg.refchannel = 'all'; % average reference
data_eeg = ft_preprocessing(cfg);
% settings for all other channels
cfg.channel = {'all', '-MEG', '-EEG'};
cfg.demean = 'no';
cfg.reref = 'no';
data_other = ft_preprocessing(cfg);
cfg = [];
cfg.resamplefs = 300;
data_meg = ft_resampledata(cfg, data_meg);
data_eeg = ft_resampledata(cfg, data_eeg);
data_other = ft_resampledata(cfg, data_other);
%% append the different channel sets into a single structure
rundata{run} = ft_appenddata(cfg, data_meg, data_eeg, data_other);
clear data_meg data_eeg data_other
end % for each run
%% append the 6 runs into a single structure
data = ft_appenddata(cfg, rundata{:});
%% compute the overall average and condition-specific averages
cfg = [];
cfg.trials = find(data.trialinfo==1);
avg_Famous = ft_timelockanalysis(cfg, data);
cfg.trials = find(data.trialinfo==2);
avg_Unfamiliar = ft_timelockanalysis(cfg, data);
cfg.trials = find(data.trialinfo==3);
avg_Scrambled = ft_timelockanalysis(cfg, data);
cfg.trials = find(data.trialinfo==1 | data.trialinfo==2);
avg_Faces = ft_timelockanalysis(cfg, data);
cfg = [];
% cfg.layout = 'neuromag306all.lay';
cfg.layout = 'neuromag306mag.lay';
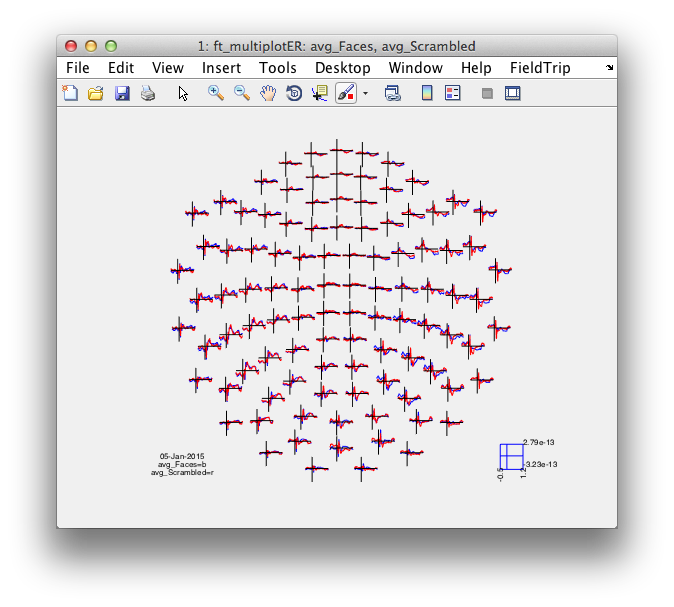
figure; ft_multiplotER(cfg, avg_Faces, avg_Scrambled);
%% compute the difference between faces and
cfg = [];
cfg.parameter = 'avg';
cfg.operation = 'x1-x2';
avg_Faces_vs_Scrambled = ft_math(cfg, avg_Faces, avg_Scrambled);
cfg = [];
% cfg.layout = 'neuromag306all.lay';
cfg.layout = 'neuromag306mag.lay';
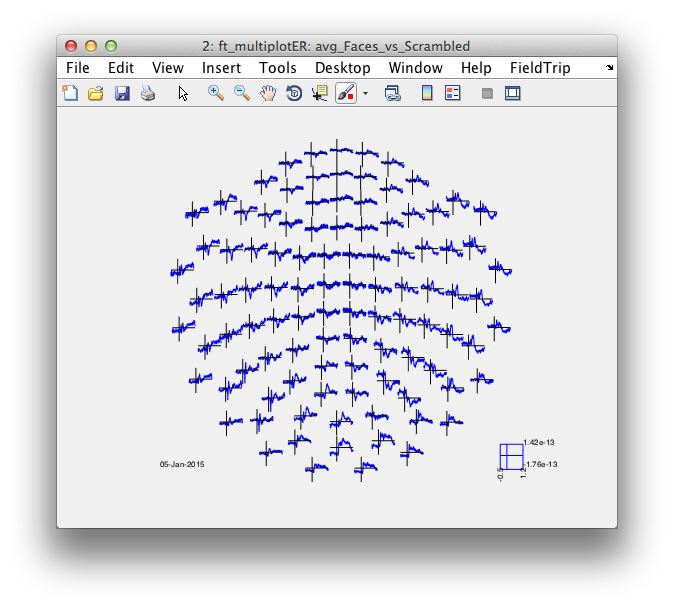
figure; ft_multiplotER(cfg, avg_Faces_vs_Scrambled);
cfg = [];
cfg.layout = 'neuromag306mag.lay';
cfg.colorbar = 'yes';
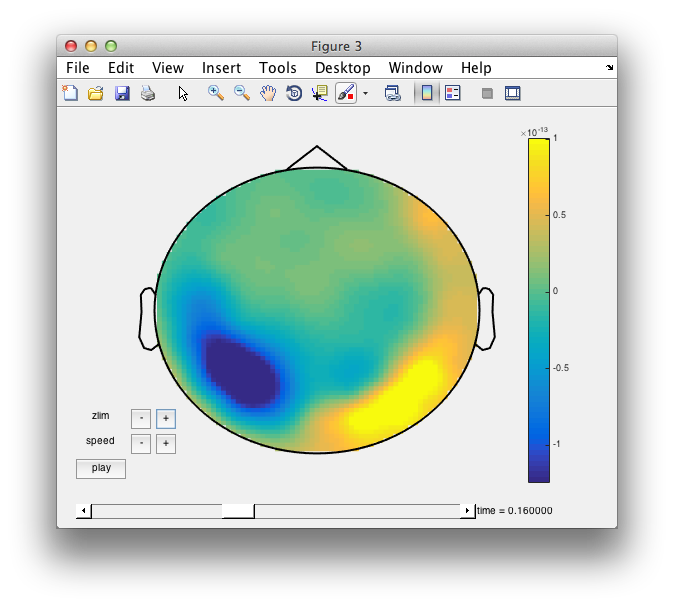
figure; ft_movieplotER(cfg, avg_Faces_vs_Scrambled);
% for saving to disk
prefix = sprintf('Sub%02d', subj);
%% save the raw data to disk
save([prefix '_raw'], 'data');
%% save the averages to disk
prefix = sprintf('Sub%02d', subj);
save([prefix '_avg_Famous'], 'avg_Famous');
save([prefix '_avg_Unfamiliar'], 'avg_Unfamiliar');
save([prefix '_avg_Scrambled'], 'avg_Scrambled');
save([prefix '_avg_Faces'], 'avg_Faces');
save([prefix '_avg_Faces_vs_Scrambled'], 'avg_Faces_vs_Scrambled');
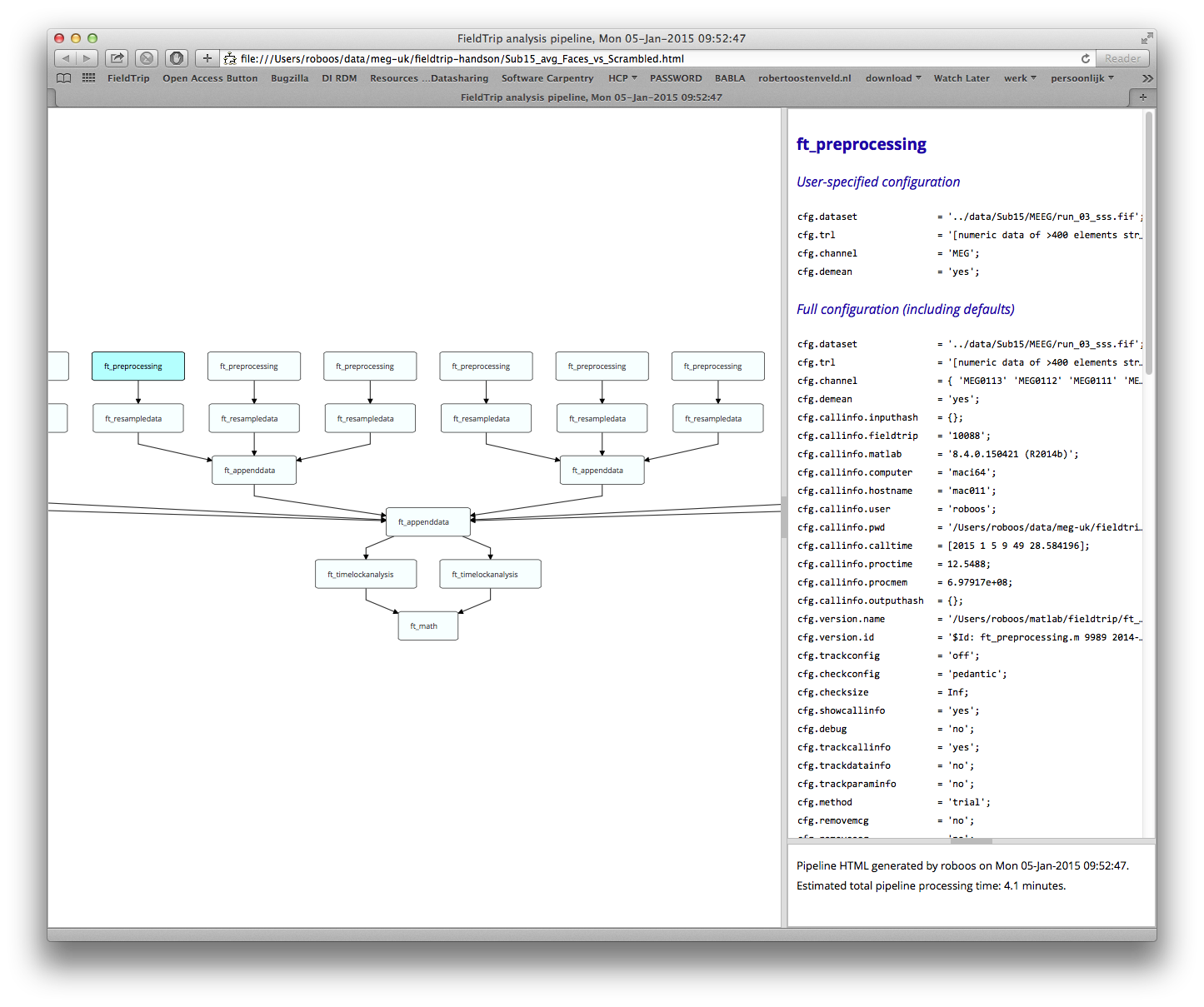
%% look at the analysis history
cfg = [];
cfg.filename = [prefix '_avg_Faces_vs_Scrambled.html'];
ft_analysispipeline(cfg, avg_Faces_vs_Scrambled);
Part 2 - use a custom statfun
subj = 15; % CHANGE THIS NUMBER FOR EACH SUBJECT
%% load the raw data from disk
prefix = sprintf('Sub%02d', subj);
load([prefix '_raw']);
load([prefix '_avg_Faces_vs_Scrambled']);
%% reorganize the timelocked data and compute stats
cfg = [];
cfg.channel = 'MEGMAG';
cfg.keeptrials = 'yes';
timelock = ft_timelockanalysis(cfg, data);
cfg = [];
cfg.correctm = 'no';
cfg.method = 'analytic';
cfg.statistic = 'indepsamplesT'; % this is implemented in ft_statfun_indepsamplesT
cfg.design = nan(1, size(timelock.trialinfo,1));
cfg.design(timelock.trialinfo==1) = 1; % Famous faces
cfg.design(timelock.trialinfo==2) = 1; % Unfamiliar faces
cfg.design(timelock.trialinfo==3) = 2; % Scrambled
cfg.ivar = 1; % the first (and only) row of the design represents the independent variable
analytic = ft_timelockstatistics(cfg, timelock);
%% do some sanity checks
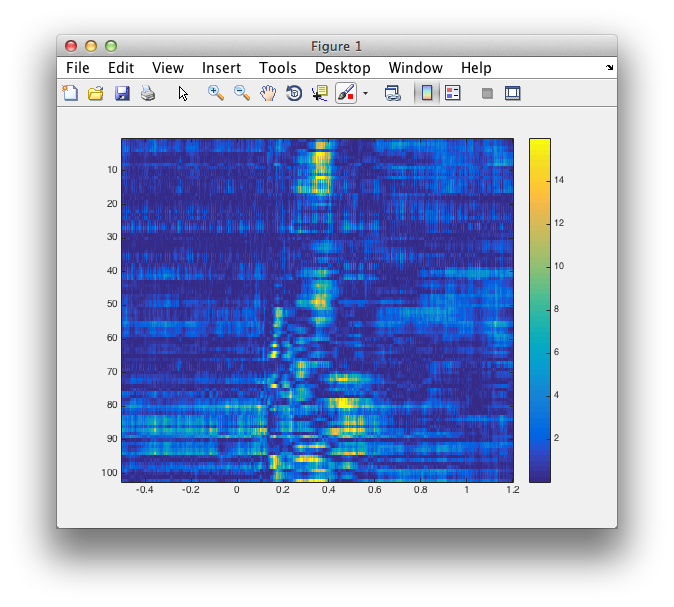
figure
imagesc(analytic.time, 1:length(analytic.label), -log10(analytic.prob))
colorbar
cfg = [];
cfg.channel = analytic.label;
tmp = ft_selectdata(cfg, avg_Faces_vs_Scrambled);
analytic.avg = tmp.avg;
% analytic.logprob = -log10(analytic.prob);
% analytic.logprob(isnan(analytic.logprob)) = 0;
% analytic.logprob(isinf(analytic.logprob)) = 10;
save analytic analytic
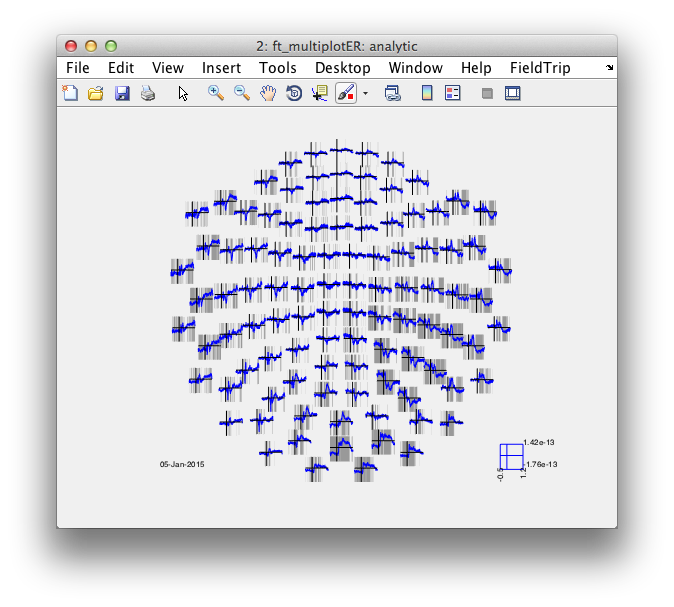
cfg = [];
cfg.layout = 'neuromag306mag.lay';
cfg.parameter = 'avg';
cfg.maskparameter = 'mask';
figure; ft_multiplotER(cfg, analytic);
%% use montecarlo and correctm=max
cfg = [];
cfg.correctm = 'max';
cfg.method = 'montecarlo';
cfg.numrandomization = 1000;
cfg.statistic = 'indepsamplesT'; % this is implemented in ft_statfun_indepsamplesT
cfg.design = nan(1, size(timelock.trialinfo,1));
cfg.design(timelock.trialinfo==1) = 1; % Famous faces
cfg.design(timelock.trialinfo==2) = 1; % Unfamiliar faces
cfg.design(timelock.trialinfo==3) = 2; % Scrambled
cfg.ivar = 1; % the first (and only) row of the design represents the independent variable
cfg.latency = [0.140 0.180];
montecarlo = ft_timelockstatistics(cfg, timelock);
save montecarlo montecarlo
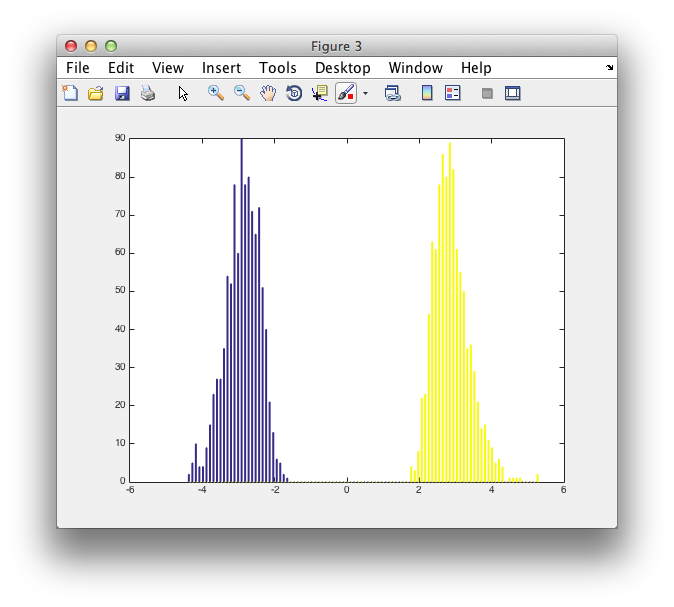
figure
hist([montecarlo.negdistribution' montecarlo.posdistribution'], 100)
%% compare the observed statistical values to the distributions
negdistribution = sort(montecarlo.negdistribution);
negthreshold = negdistribution(26) % why not at 5%, i.e. 51?
posdistribution = sort(montecarlo.posdistribution);
posthreshold = posdistribution(975) % why not at 5%, i.e. 950?
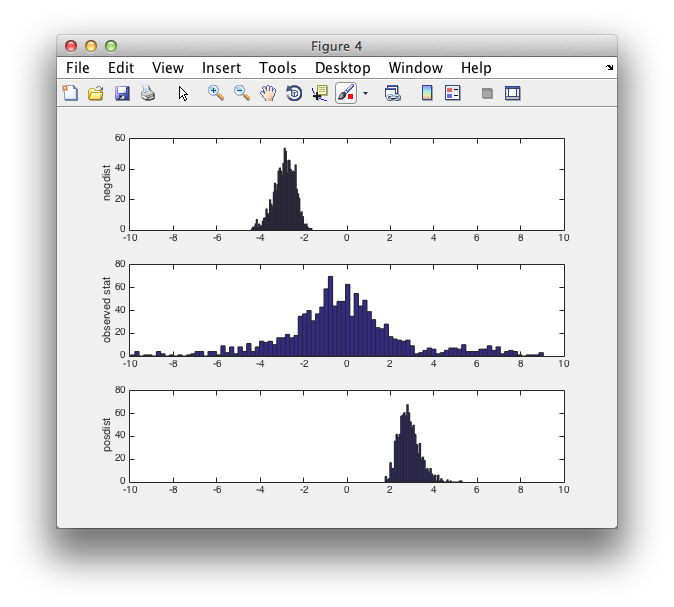
figure
subplot(3,1,1)
hist(montecarlo.negdistribution, 50)
ylabel('negdist');
xlim([-10 10]);
subplot(3,1,2)
hist(montecarlo.stat(:), 100)
ylabel('observed stat');
xlim([-10 10]);
subplot(3,1,3)
hist(montecarlo.posdistribution, 50)
ylabel('posdist');
xlim([-10 10]);
%% use your own trialfunction, e.g., spearman rank correlation
cfg = [];
cfg.channel = 'MEG2021';
cfg.statistic = 'statfun_parametric';
cfg.design = nan(1, size(timelock.trialinfo,1));
cfg.design(timelock.trialinfo==1) = 1; % Famous faces
cfg.design(timelock.trialinfo==2) = 2; % Unfamiliar faces
cfg.design(timelock.trialinfo==3) = 3; % Scrambled
cfg.ivar = 1; % the first (and only) row of the design represents the independent variable
cfg.correctm = 'no'; % or another method
cfg.method = 'analytic';
analytic2 = ft_timelockstatistics(cfg, timelock);
cfg.correctm = 'max';
cfg.method = 'montecarlo';
cfg.numrandomization = 1000;
montecarlo2 = ft_timelockstatistics(cfg, timelock);
figure
hold on
plot(analytic2.time, -log10(analytic2.prob), 'b')
plot(montecarlo2.time, -log10(montecarlo2.prob), 'r')
line([montecarlo2.time(1) montecarlo2.time(end)], [1.3 1.3])
save analytic2 analytic2
save montecarlo2 montecarlo2
Appendix - statfun_parametric
function stat = statfun_parametric(cfg, dat, design)
% STATFUN_PARAMETRIC
%
% This function supports
% cfg.ivar = number
% cfg.type = string
% specify the defaults for the options
cfg.type = ft_getopt(cfg, 'type', 'Spearman');
cfg.ivar = ft_getopt(cfg, 'ivar', 1);
trialcode = design(cfg.ivar,:);
% [rho, pval] = corr(trialcode', dat', 'type', 'Spearman');
% [rho, pval] = corr(trialcode', dat', 'type', 'Pearson');
% [rho, pval] = corr(trialcode', dat', 'type', 'Kendall');
[rho, pval] = corr(trialcode', dat', 'type', cfg.type);
stat.stat = rho; % this is sufficient for method=montecarlo
stat.prob = pval; % this is required for method=analytic